ETHOXYLATED COCOALKYL AMINE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
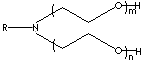
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Ethomeen C; Polyoxyethylene Cocoalkyl Amines; Polyethoxylated Cocoalkyl Amine; Ethanol, 2,2'-Iminobis-, N-Kokos-alkylderivate (German); Eanol, 2,2'-iminobis-, N-coco alquil derivados (Spanish); éthanol, imino-2,2' bis-, dérivés N-alkyles de coco (French);
CLASSIFICATION
SURFACTANTS /
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
amber liquid, amine odor
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
- HLB numbers describe following characterestics:
- <10 : Lipid soluble (or water-insoluble)
- >10 : Water Soluble
- 4-8 : Antifoaming
- 7-11 : Water-in-oil emulsion
- 12-16 : Oil-in-water emulsion
- 11-14 : Good Wetting
- 12-15 : Good detergency
- 16-20 : Stabilizing
- HLB values of fatty acid compounds are:
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Esters are non-toxic and non-irriting nonionic emulsifiers. They are prepared by the esterification of fatty acids with polyethylene glycols. The low molecular weight ranging PEG Esters are oil-soluble to work in nonaqueous systems. The high molecular esters are water-soluble can be used in aqueous systems. Polyethylene Glycol Esters are used as emulsifiers and in formulating emulsifer blends, thickener, resin plasticizer, emollient, opacifier, spreading agent, wetting and dispersing agent, and viscosity control agents. They also have application in the metalworking, pulp, paper, textile and as defoamers for latex paints.
Ethoxylated fatty amines are nonionic surfactants used as an emulsifier and in formulating emulsifier blends. Used as a wetting agents, dispersants, stabilizers, sanitizers and defoaming agents. End applications include agrochemical emulsifiers, industrial cleaners, metal cleaners, textiles, paper de-inking, drilling products and detergents. Used as an intermediate for the synthesis of anionic surfactants.
SALES SPECIFICATION
POE 2
APPEARANCE
HLB
6.6
MOISTURE
1.0% max
TERT. AMINE
97.0% min
POE 5
APPEARANCE
HLB
10.5
MOISTURE
1.0% max
TERT. AMINE
98.0% min
POE 15
APPEARANCE
HLB
15.5
MOISTURE
1.0% max
TERT. AMINE
98.0% min
Nonionic surfactants are surface active agents which do not dissociate into ions in aqueous solutions, unlike anionic surfactants which have a negative charge and cationic surfactants which have a positive charge in aqueous solution. Nonionic surfactants are more widely used as detergents than ionic surfactants because anionic surfactants are insoluble in many hard water and cationic surfactants are considered to be poor cleaners. In addition to detergency, nonionic surfactants show excellent solvency, low foam properties and chemical stability. It is thought that nonionic surfactants are mild on the skin even at high loadings and long-term exposure. The hydrophilic group of nonionic surfactants is a polymerized alkene oxide (water soluble polyether with 10 to 100 units length typically). They are prepared by polymerization of ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and butylene oxide in the same molecule. Depending on the ratio and order of oxide addition, together with the number of carbon atoms which vary the chemical and physical properties, nonionic surfactant is used as a wetting agent, a detergent, or an emulsifier. Nonionic surfactants include alcohol ethoxylates, alkylphenol ethoxylates, phenol ethoxylates, amide ethoxylates, glyceride ethoxylates (soya bean oil and caster oil ethoxylates), fatty acid ethoxylates, and fatty amine ethoxylates. Another commercially significant nonionic surfactants are the alkyl glycosides in which the hydrophilic groups are sugars (polysaccharides).